What Is a Hypoplastic Uterus? – Causes, Treatment, and Pregnancy Progress
Congenital or acquired underdevelopment of the uterus, i.e., hypoplastic uterus, is a rare pathology in less than 5% of women. The uterus is a hollow organ where conception and fetus development occur. Its various diseases can cause infertility or miscarriage. But due to poor ecology, early onset of sexual activity, and alcohol abuse in adolescence, such a diagnosis is increasingly happening for young nulliparous girls.
What Is Uterine Hypoplasia?
At birth, the length of the uterus is no more than 3 cm. Gradually, it increases in size, and by the end of puberty, it should reach 7 cm. The length of the narrowest part – the cervix, is normally 2.5 cm. Lower rates are characteristic of a pathological condition – hypoplasia. Due to insufficient or weak development, such a uterus is also called a naive or infantile uterus.
A woman’s reproductive organ has a body, a cervix, appendages (ovaries and fallopian tubes), and an isthmus. Any of these departments may begin to lag behind in development. Therefore, medics distinguish several types of hypoplasia.
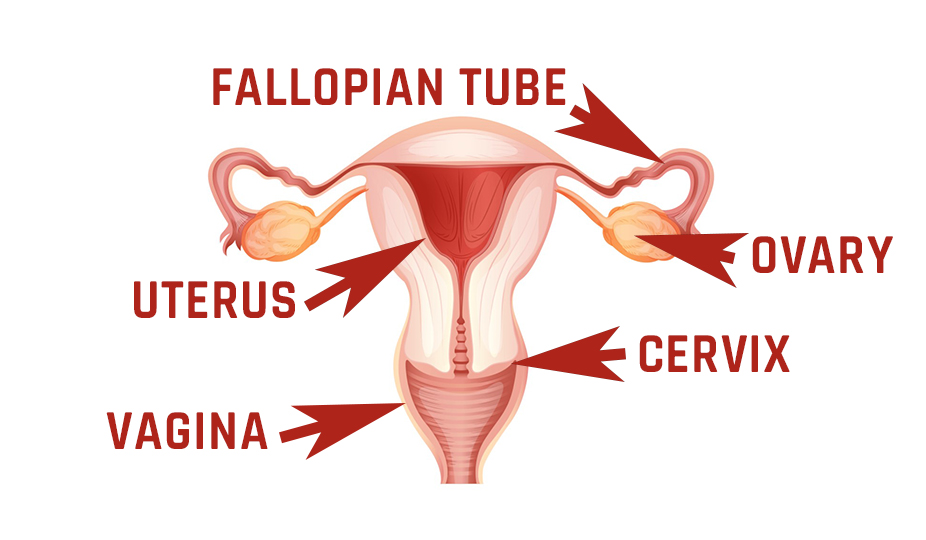
Nota Bene! With this diagnosis, they reveal only a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the physiological norm for the given age. The organ itself is developed correctly, without defects.
The hypoplastic uterus can be an independent diagnosis and manifest other diseases in the body.
What Causes Hypoplastic Uterus?
The main causes of acquired hypoplasia are hormonal disorders. The pituitary gland, ovaries, and hypothalamus produce sex hormones. Any failures in their work can lead to a delay in a girl’s puberty.
All factors that can cause hormonal disruptions can be divided into two groups.
External Uterine Hypoplasia Causes
- surgical manipulations on the genitals in childhood or adolescence;
- disruption of the central nervous system as a result of injury or disease;
- heavy physical activity, such as professional sports;
- malnutrition, diets during puberty;
- bad habits, teenage alcoholism is especially dangerous.
Internal Uterine Hypoplasia Causes
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- malignant formations;
- congenital malformations of the liver and heart;
- kidney failure;
- autoimmune diseases;
- ovarian failure;
- unfavorable heredity.
This pathology can also occur congenitally. In this case, this is due to adverse factors’ influence on a pregnant woman’s body. Sexual characteristics in the fetus begin to form within a few weeks after conception. During this period, a woman may still not know about pregnancy. Therefore, smoking, alcohol, medication, or infectious diseases can provoke negative factors that can cause disturbances in the process of forming the sex of the fetus.
Strong emotional upheavals can also harm the hormonal system and cause disruptions.
A naive uterus can become deformed over time. It develops an inflection of the upper part, and the cervical canal takes the form of a cone.
Uterine Hypoplasia Symptoms
It is possible to suspect this disease only with the onset of puberty. One of the important manifestations is the absence of menstruation in a girl until age 15-16 and the weak formation of secondary sexual characteristics.
Usually, with such a diagnosis, there is also a physical lag in development. Growth and weight significantly below the age norm, excessively narrow pelvic bones, asthenic physique, and underdeveloped mammary glands are diagnosed.
Other symptoms of uterine underdevelopment are as follows.
- Irregular or painful menstruation.
- Lack of libido.
- Problems with conceiving a child.
- Lack of hairline or weak hair growth in the pubic area.
- Frequent inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
- Miscarriage. Miscarriages always occur early.
- Weak labor activity of the uterus.
- The occurrence of more than two consecutive ectopic pregnancies.
- Anorgasmia.
Manifestations depend on the degree of underdevelopment of the reproductive organ. The most severe is the first degree. Here menstruation is completely absent (amenorrhea). Either the discharge is scarce and occurs at large time intervals.
Hypoplastic Uterus Degrees and Their Characteristics
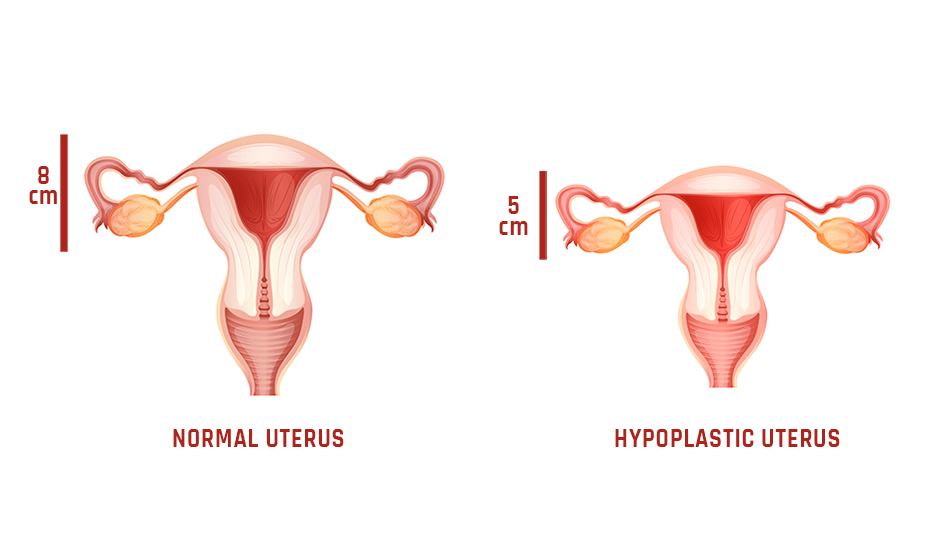
The severity of the disease and the success of treatment depend on the uterus size. There are three degrees of pathology.
1. First Degree
1st degree or rudimentary stage of development is most often a congenital pathology. The organ size is like that of a newborn girl and is 3 cm. At this stage, the uterine cavity and appendages are absent, excluding the possibility of menstruation. Therefore, pregnancy and childbearing with such a uterus are excluded. Conservative therapy is ineffective.
2. Second Degree
2nd degree or infantile (naive) uterus is the most common type. The organ stopped developing by 4-5 cm. At the same time, it has a physiologically correct structure and cavity. The treatment is long. The chance of pregnancy is small.
3. Third Degree
3rd degree or adolescent stage – has a favorable prognosis with the right treatment. For this degree, the uterus size is 5-7 cm, almost on the border of normal values. With small deviations, the pathology can go away on its own during the first pregnancy since the size of the uterus after childbirth increases slightly.
T-shaped uterus (Ia) has a correlation of two-thirds uterine corpus and one-third cervix while infantilis (Ib) has an inverse correlation pic.twitter.com/30sxMjZOEE
— Hysteronews 1,5 K (@hysteronews) September 20, 2018
Only a gynecologist can determine the degree of pathology during an examination. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the likelihood of reproductive function restoration. Therefore, it is important to educate girls about the peculiarities of the course of sexual development. In case of any deviations, it is necessary to consult a pediatric gynecologist.
Hypoplastic Uterus Treatment
With a hypoplastic uterus, external labia also often underdevelop. The gynecologist notices these violations during the examination and studies the patient’s history. One also measures the girl’s height, weight, and hips size.
It is possible to accurately determine the size of the uterus and the degree of pathology only with the help of vaginal ultrasound. Be sure to appoint hormonal research, which will help to determine the level of sex hormones accurately.
Also, the doctor may prescribe the following types of diagnostics:
- MRI.
- X-ray of the hand – to determine bone age.
- Probing of the uterine cavity.
- Colposcopy.
One should consult related specialists – an endocrinologist, a neurologist, and a urologist.
Conservative treatment works only with 2 and 3 degrees of the hypoplastic uterus. The basis is hormonal therapy. Medicines are selected only by a doctor. One considers the patient’s age, the organ’s size, and menstrual and reproductive function violations. To reduce severe menstrual pain or PMS, doctors prescribe symptomatic treatment.
Additionally, experts use physiotherapeutic treatment. The following procedures are effective:
- ozone therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- laser exposure;
- galvanization;
- ultraviolet radiation.
These procedures improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs and reduce inflammation. They can also prescribe gynecological massage and physiotherapy exercises. Only individual complex treatment can lead to a positive result.
Forecast
If a 1st degree of the disease is detected, no treatment can lead to natural conception. If the ovaries are functioning, the doctor recommends IVF. But since the cavity is not formed with a rudimentary uterus, problems will arise with the bearing of the fetus. It is where surrogacy can help.
With 2nd degree in pathology, there is a small chance of conception and pregnancy. Even if conception occurs, pregnancy and childbirth can occur with complications.
A favorable prognosis can only be at the 3rd stage when minimal deviations in the uterus development are diagnosed. But the treatment should be under the supervision of a physician.
It is important to detect pathology as early as possible. In puberty, hypoplasia can be cured without resorting to hormone therapy. Proper nutrition, a course of vitamins, and a healthy lifestyle can restore disturbed hormonal levels.
FAQ – What You Need to Know about Hypoplastic Uterus

Of course, a skinny physique is not always a sign of this medical condition. But if along with it you see that your daughter does not have periods, although she is already 15, this is an alarming bell, and you should consult a gynecologist.
Of course not! Moreover, even if a woman’s uterus is less than normal, but the width is normal, there is a sufficient layer of the endometrium; she may never know about this condition. She gets pregnant and gives birth. Sometimes, she needs special therapy because pregnancy does not always go smoothly.
Many have a very strong toxicosis and must undergo special treatment in a hospital. When bleeding suddenly opens, the most dangerous thing is the threat of miscarriage. But again, timely therapy helps to maintain pregnancy in 90% of cases.
Everything is possible! Properly selected hormone therapy works wonders. From 3 to 6 months, the uterus increases to the desired size. If there are concomitant pathologies – polycystic ovary syndrome or tubal obstruction – an integrated approach to treatment using laparoscopy is required.