Infertility Common Causes – Facts About Male And Female Infertility
The desire to have children is one of the human’s most natural aspirations. You do not have to feel embarrassed or ashamed because you cannot conceive or carry a pregnancy – these destructive feelings will only keep you away from seeking timely infertility treatment. That`s why in this post we will discuss the most infertility common causes as well as possible treatment and IVF solutions.

What Is Infertility?
Infertility is a reproductive system`s disorder that can be triggered by a series of reasons and medical conditions and touches about one in six women and men of reproductive age. Leading reproductive health organizations advise consulting with an infertility expert if you fit into one of the groups below:
- Women under 35 years of age who have not been successful in getting pregnant after 12 months of unprotected sexual activities.
- Those who are 35 years of age and older who have not been successful in getting pregnant after 6 months of deliberate conceiving efforts or more.
- Women who have experienced at least two miscarriages.
- Those who have been diagnosed with the polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis or have a male partner with a low sperm count, which is an impairing factor in a woman`s s ability to conceive.
Infertility Common Causes Statistics
It`s not just you – over 50 million individuals worldwide experience fertility problems. Infertility can hit women and men alike; some couples have several diagnoses impacting both partners while others face what many believe to be the most confusing diagnosis: unexplained infertility.
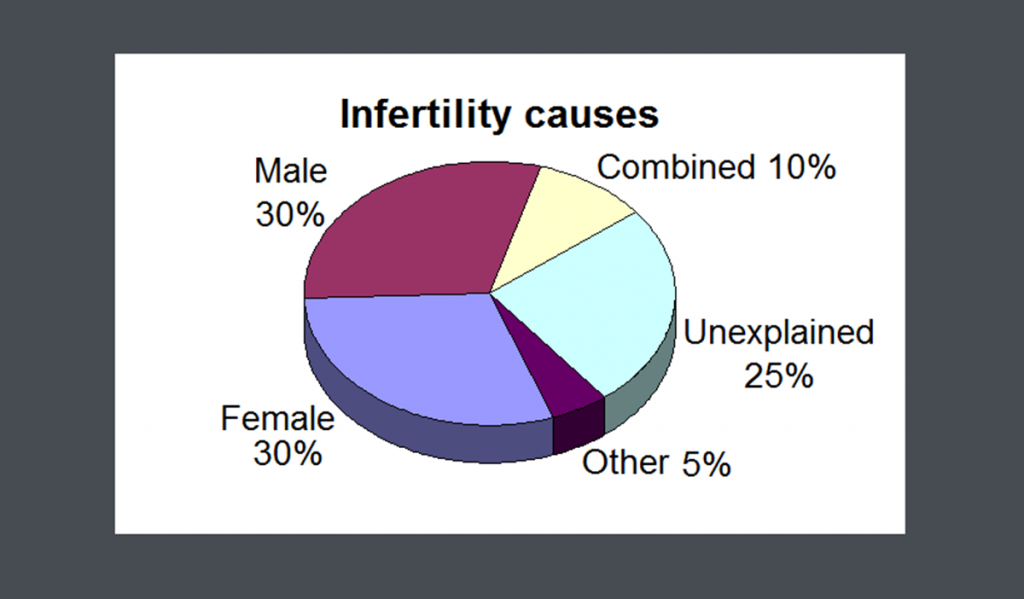
Some Common Causes Of Infertility – Classification
There are multiple infertility common causes, but they can be classified around the following issues: egg quality and ovulation; sperm quality and function; fertilization; as well as implantation.
Problems With Menstrual Cycle And Ovulation
Anovulation – abnormal or irregular ovulation – is one of the most prevalent causes of female infertility and some 25% of all female infertility cases can be attributed to this problem.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a painful and, when left untreated, chronic condition characterized by lining tissues of uterus getting outside the uterus, possibly inside the fallopian tubes, peritoneal cavity of the ovaries, bladder or bowels. The scar tissue resulting from this condition can trigger infertility. The treatments methods that are effective in infertility patients with endometriosis include in vitro fertilization (IVF) as well as surgery.
The Fallopian Tubal Disease
Fallopian tubes represent a pair of tubes alongside which eggs are being transported from the ovaries to the uterus where the fertilization happens. The fallopian tubes can get blocked due to a few factors including scarring and infection. When a blockage strikes, fertility may become endangered. In vitro fertilization has been long used to help women with the fallopian tubal disease to regain fertility.
Fibroids
Fibroids are the estrogen-dependent non-cancerous benign tumors that build inside the uterus and may cause heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pains. Fibroids can also cause recurrent miscarriages and infertility. A gynecologist might recommend a myomectomy (removal of fibroids) as the optimal surgical intervention for patients who want to get pregnant.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
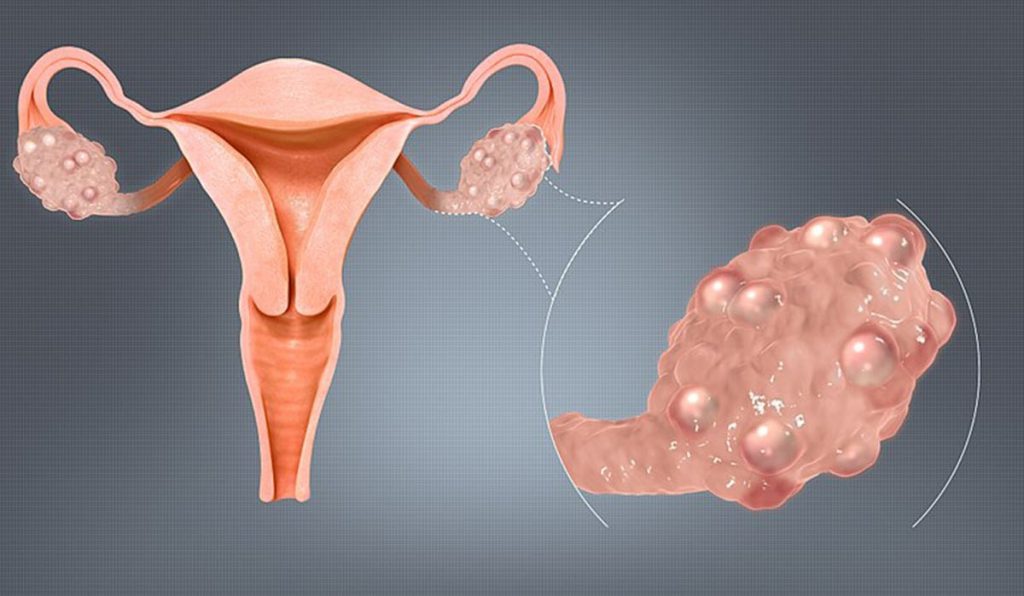
PCOS is a hormonal disorder resulting in either irregular or no periods or heavy menstrual periods, excess facial and body hair, acne, obesity, and pelvic pain. Characterized by the appearance of many tiny follicular cysts in the ovary visible at ultrasound examination, PCOS might make it harder for affected women to get pregnant and carry a pregnancy. Medication therapy, weight loss, and techniques like intrauterine insemination (IUI) and IVF can help PCOS patients.
Premature Ovarian Failure
Sometimes women who are 40 years old or younger develop a condition when their ovaries can no longer ovulate eggs. Known as a premature ovarian failure (POF), this condition is not equivalent to premature menopause. The affected women may not only potentially lose their reproductive capabilities, but also develop a greater risk for osteoporosis and heart disease. Several medical conditions can trigger POF, but physicians cannot always identify one.
Older Intended Mothers
No matter how good a woman feels or looks, her ovarian function declines in both quality and quantity as a woman ages. Therefore, it is essential for women who are over 40 to seek medical assistance after three months of pregnancy attempts. Your ability to ovulate does not always translate into your ability to get pregnant.
Secondary Infertility
After having one or two children successfully, some couples are confused by their failure to conceive again. Secondary infertility can be just as demoralizing as primary infertility and partners often do not reach out for the support they need because of guilt or fear.
Taking the medication
Oligospermia (insufficient number of sperm cells) and azoospermia (no sperm produced at all) are the two most common reasons for male factor infertility. Further infertility common causes include sperm cells that perish before they reach the egg or malformed sperm cells. Occasionally, male factor infertility is attributable to a chromosomal abnormality or genetic disease.
Additional reasons for male infertility include inherited absence of the vas deferens, a tube that conveys sperm from the testicles to the urethra for ejaculation. It can also be varicoceles, an abnormal enlargement of the varicose veins in the scrotum, which drains blood from the testicles and inhibits normal function; cryptorchidism or hidden testicles, also an inherited condition; as well as a prior vasectomy that must be reversed.
Infertility Common Causes – Final Words
The main thing you should remember is that primary or secondary infertility is not the end of the story. There are dozens of treatment techniques, as well as other alternatives, like IVF, egg and sperm donation, etc. If you would like to know more about them – check our services pages or get a free consultancy from our fertility experts.