IVF hCG Levels – How to Detect Prgnancy with a Test
In vitro fertilization allows many couples to realize their dream of parenthood. But there are many questions and milestones along the way. One of them is hCG. IVF hCG levels begin to increase 6-12 days after fertilization. The range from 5 to 1000 mIU/mL means the first positive pregnancy test results.
Is it important to monitor it after embryo transfer? How and why does this hormone play such an essential role? And what to do if the indicators aren’t quite as expected? We invite you to figure out how to interpret the IVF hCG levels correctly and why it is so crucial for the chance of a healthy pregnancy. If you are going through IVF, this material will be valuable!
What is IVF?
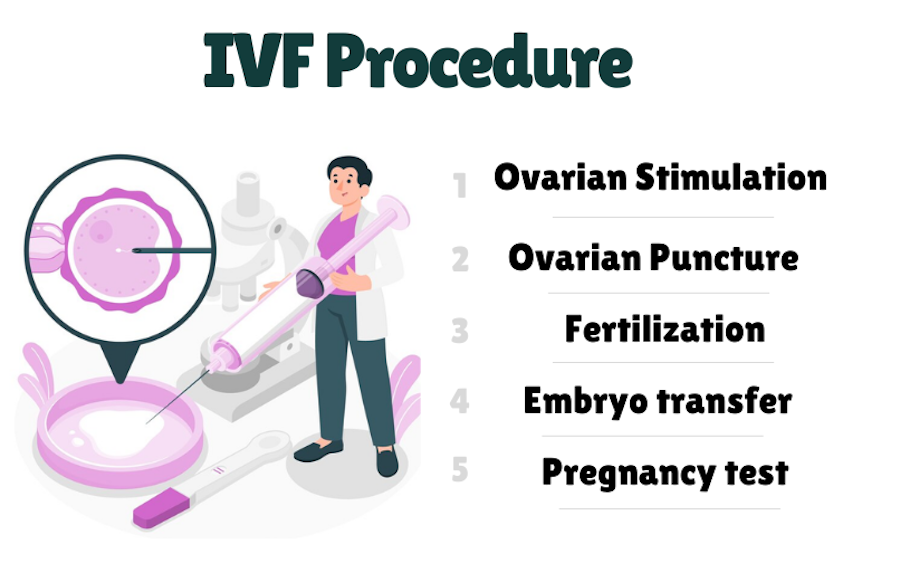
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is one of the most common and effective medical procedures for treating infertility. Although many people know about IVF, not everyone fully understands it. Let’s find out what kind of procedure it is, who needs it, and how the whole process goes.
What Happens During the Procedure?
IVF is a process in which the egg is fertilized outside the woman’s body, not in it. More precisely, in a lab. It all starts with giving a woman hormonal drugs. They stimulate the production of several eggs instead of the usual one or two. These eggs are then retrieved from the ovaries through a small surgery.
The next step is egg fertilization with sperm. There are several options here: conventional in vitro fertilization or fertilization using intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). This technique involves injecting a sperm directly into an egg.
After the embryo is formed, it is transferred to the woman’s uterus, where it should fix and start developing.
Who Needs IVF?
IVF is recommended for couples who have problems conceiving naturally. The following infographic shows the issues that are reasons for IVF.
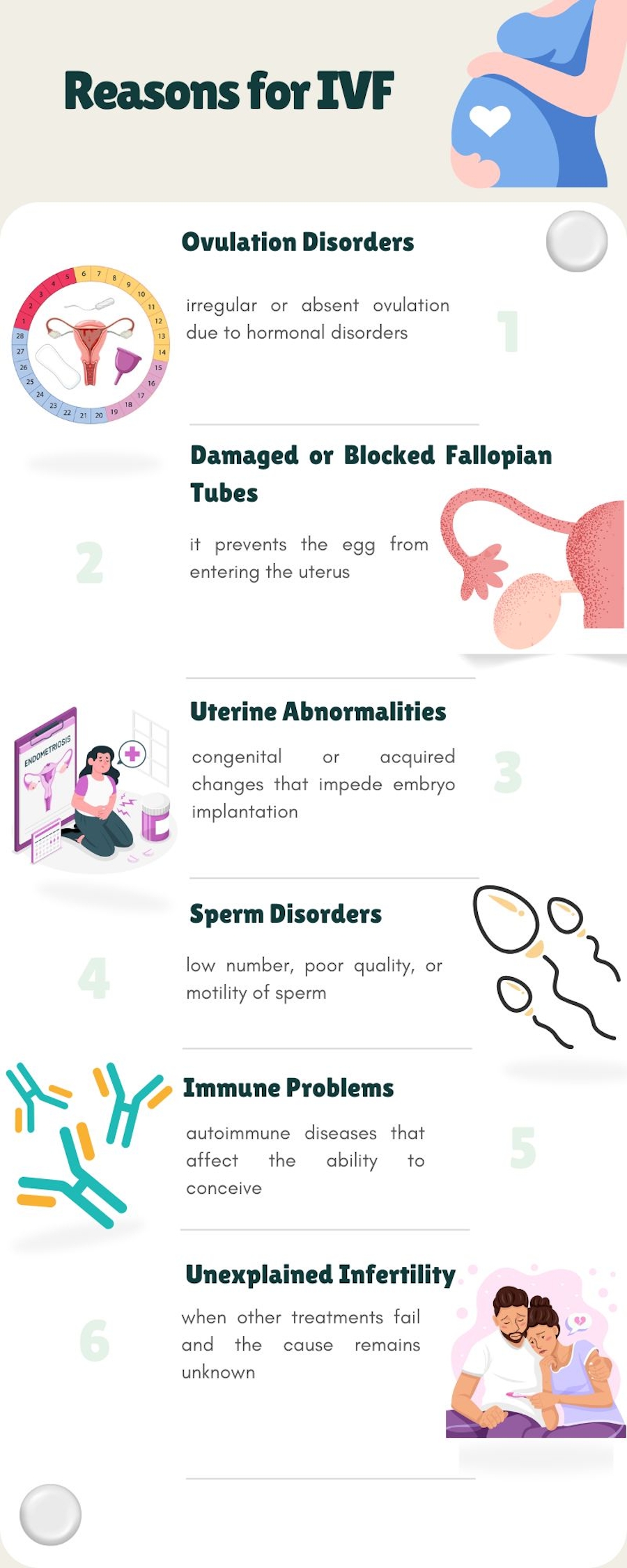
IVF is not just a technology, it is a real way out of a situation where natural pregnancy doesn’t work. Although the procedure isn’t 100% successful, for many people, it is the only chance to have a baby. Of course, there is still the option of using surrogacy services. After all, this is a very common practice now that allows everyone to experience the pleasure of parenthood.
What is hCG?
Human chorionic gonadotropin is among the most vital hormones produced by the body during pregnancy. Let’s understand how this hormone works, what functions it has in the organism, and why it is an effective marker for pregnant women’s health.
So, the hCG hormone is produced by the cells of the chorion (future placenta) immediately after egg fertilization. The hCG doesn’t appear in a woman’s body before fertilization occurs, so its level can be the first signal of pregnancy.
Basic hCG Functions
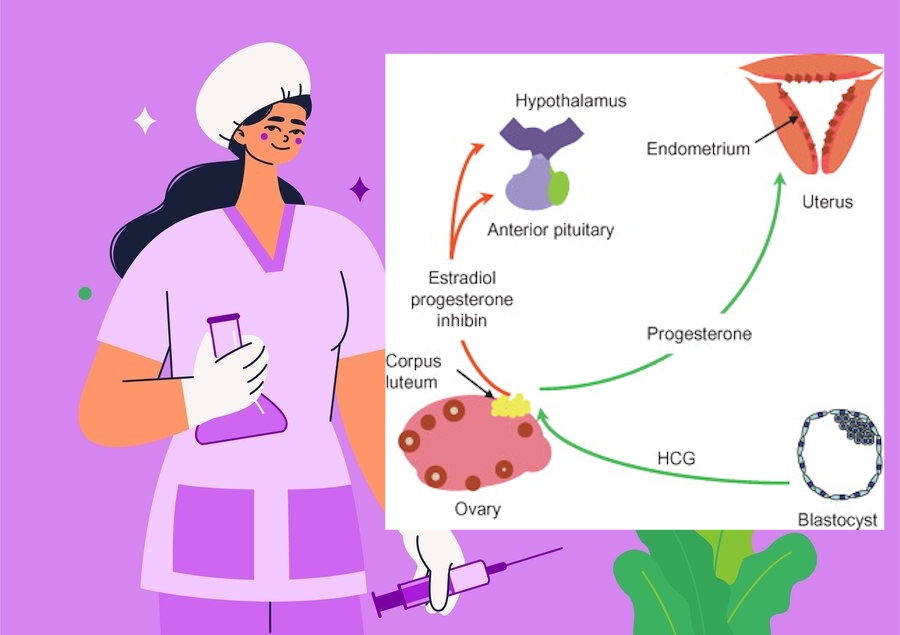
Maintenance of the corpus luteum
One of the main functions of hCG is to support the corpus luteum, which is formed after ovulation. The corpus luteum is a source of progesterone in the first weeks of pregnancy. Progesterone, in turn, supports the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterus), making it suitable for the implantation of a fertilized egg. The hCG, produced in the early stages of pregnancy, prevents the degradation of the corpus luteum by maintaining its hormonal activity.
Stimulation of placental development
When pregnancy is developing steadily, the hormone activates placental cells. This promotes its growth and further supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. The placenta begins to actively produce other essential hormones (for example, estrogen and progesterone) that contribute to a healthy pregnancy.
Ensuring normal embryo development
The hormone affects numerous biochemical processes necessary for the proper development of the embryo. It maintains the immune tolerance of the mother’s body to the fetus since the fetus is partially genetically different from the mother. Thanks to hCG, the mother’s body doesn’t reject the fetus, so it can develop normally.
Effect on the synthesis of other hormones
The hCG stimulates the production of other hormones that are essential for maintaining pregnancy. For example, it helps to increase the level of estrogen, ensuring the proper functioning of the mother’s reproductive organs and helping to prepare the body for childbirth.
How does hCG Act in the Body?
This hormone acts through a specific receptor, the hCG receptor, which is located on the surface of cells. This receptor belongs to a large group of receptors that respond to gonadotropin hormones. When hCG binds to the receptor, a variety of biochemical signaling pathways are activated to help maintain pregnancy and fetal development.
One of the main mechanisms is the stimulation of an intracellular process that includes adenylate cyclase cycles and cyclic AMP production. This process activates the progesterone synthesis in the corpus luteum and increases the blood supply to the uterus. It maintains the conditions necessary for normal embryo growth.
Specifics of IVF hCG Levels
During in vitro fertilization, the hormone is used to monitor the success of embryo implantation. Immediately after the embryo is transferred to the uterus, doctors monitor hCG levels to see if the embryo has attached to the uterine wall and if a pregnancy is developing. By the way, you can read more about the transfer procedure and what to expect from your body via this link.
If we look at it in more detail, the impact is as follows.
Support for Embryo Implantation
After the embryo is transferred to the uterus during the IVF procedure, it needs to attach to the uterine wall to start developing. For this, the woman’s body must provide certain hormonal conditions. HCG is actively produced by chorionic cells (part of the placenta that begins to form after successful implantation). The hormone signals to the body that pregnancy has occurred and that the corpus luteum needs to be maintained. The corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone under the influence of hCG.
Marker of Implantation Success
The hCG level in a woman’s blood is measured to determine whether fertilization has been successful and whether pregnancy has begun. After the embryo is transferred into the uterus, a hCG test can be done a few days later. This helps the doctor determine whether implantation has begun.
Determining Possible Complications
If the hormone level doesn’t rise as fast as expected or remains low, it may indicate implantation problems or even an ectopic pregnancy. This gives the doctor the ability to take action in time and correct the treatment.
Understanding hCG Levels
When you just become pregnant, the hCG level in your blood starts to rise very quickly. It doubles every 48-72 hours for the first two weeks after the embryo implants. So, you may have hormone results in the range shown here:
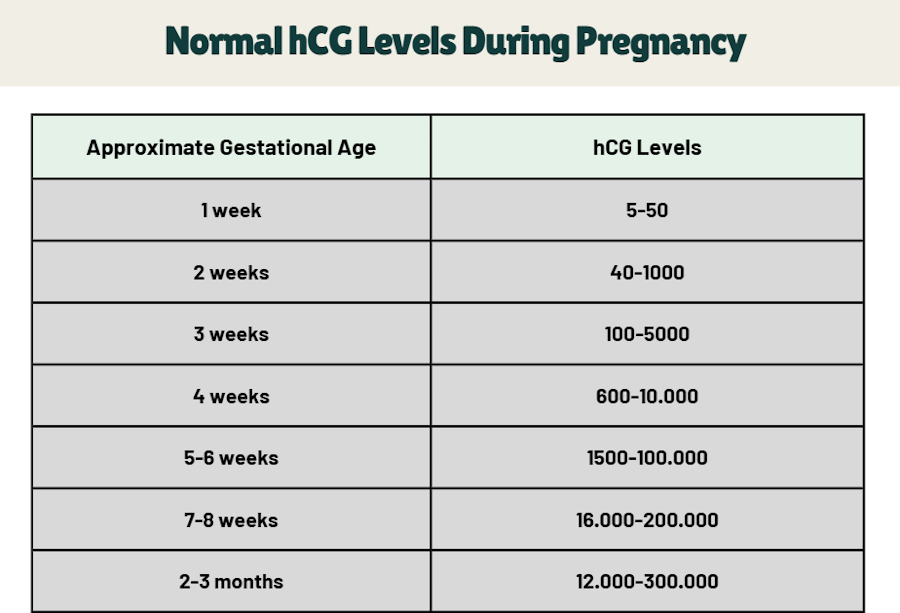
Let’s take a closer look at the table:
- Initial levels (1-2 weeks after fertilization): Immediately after fertilization, hCG doesn’t appear in your blood yet. It is only after the embryo attaches to the uterine wall (this happens about 6-12 days after fertilization) that hCG levels begin to increase. At this point, you may already see the first positive pregnancy test results. HCG levels range from 5 to 1000 mIU/mL. And this is just the beginning!
- The first peak (2-4 weeks of pregnancy): At 2-3 weeks of pregnancy, hCG levels can increase to 5000 mIU/ml, and as we said, it doubles every 48-72 hours. At this time, you can confirm your pregnancy with an hCG test, which will show a higher result.
- The highest level (4-6 weeks): Now hCG levels reach 100,000 mIU/ml or even more. This means that your pregnancy is developing actively, and the placenta has already begun to function at full strength.
- Rise and fall (7-12 weeks): After 6-7 weeks, hCG levels begin to stabilize or even decline. This decline is normal because the placenta has already developed enough and begins to produce the necessary hormones. After that, the hCG level no longer increases but only fluctuates between 20,000-200,000 mIU/ml until the end of the first trimester.
- Beyond 12 weeks of pregnancy: After 12 weeks of pregnancy, hCG levels stabilize again and begin to decline. This indicates that the body has adapted to the new conditions and the pregnancy is entering the second trimester.
How to Interpret HCG Levels Properly?
Sometimes, hCG levels can be difficult to understand without context. But for doctors, it is a tool for identifying pathology and problems or establishing a successful pregnancy. The study points to the following relationship between hormone levels and pregnancy issues:
| Beta hCG | Biochemical Pregnancy | Miscarriage | Ectopic Pregnancy | Ongoing Pregnancy |
| <100 | 48.00% | 20.00% | 8.00% | 24.00% |
| 101-200 | 26.67% | 22.22% | 11.11% | 40.00% |
| 201-300 | 2.50% | 27.50% | 10.00% | 60.00% |
| 301-400 | 0.00% | 22.22% | 5.56% | 72.22% |
| 401-500 | 4.08% | 6.12% | 2.04% | 87.76% |
| 501-600 | 5.71% | 14.29% | 5.71% | 74.29% |
| 601-1000 | 0.82% | 14.75% | 0.00% | 84.43% |
| 1001-2000 | 0.00% | 7.80% | 0.00% | 92.20% |
| 2001+ | 0.00% | 3.33% | 0.00% | 96.67% |
But you should never diagnose yourself because there are many factors to consider when interpreting the results. Among them are:
- HCG levels are not the only indication of pregnancy health. Sometimes, it happens that the hormone level doesn’t meet the standard numbers, but the pregnancy can still be normal. It’s crucial to consider other factors, such as the general condition, symptoms, and the ultrasound results.
- Different laboratories may use different measurement methods, so the values may vary. It is important to compare results in the context of a particular laboratory and consult your doctor.
- The hCG level may vary from pregnancy to pregnancy. Each woman and each pregnancy has its norms. Therefore, don’t compare your results with other women’s tests.
To Summarize
Thus, the IVF hCG levels determine the procedure’s success. Increased or decreased levels of the hormone can indicate various problems, including the risk of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Monitoring hormone levels allows doctors to determine how a pregnancy develops after IVF. It helps to take the necessary measures to increase the chances of success. However, remember that this hormone isn’t the only criterion for assessing pregnancy status, so take a comprehensive approach to all tests and take the doctor’s advice.
We recommend that you don’t be afraid to ask doctors for advice, take tests on time, stay calm, and have a positive attitude!